Written by: <Authors><Author><Id>3006</Id><Name>Pradeep Kulshrestha</Name><AuthorImage>/3006/kul.jpg</AuthorImage><FriendlyName>pradeep-kulshrestha</FriendlyName></Author></Authors>

Written by: <Authors><Author><Id>3006</Id><Name>Pradeep Kulshrestha</Name><AuthorImage>/3006/kul.jpg</AuthorImage><FriendlyName>pradeep-kulshrestha</FriendlyName></Author></Authors>

Carbon fibre reinforced plastic (CFRP) is the advanced innovation of the20th century, says PradeepKulshrestha.
The end of the Metal Age is here.The age of carbon fibre reinforced composites has just begun. Wherever a massneeds to be accelerated or slowed down, lightweight design is urgently neededto achieve high energy efficiency. In case of an accident, CFRP absorbs abouteight times more energy than steel or aluminum do. This becomes especiallyobvious in the aviation industry. If an airplane is lightened by a kilogram,its fuel consumption is reduced by approximately 3,000 kg over its lifetime.
Carbon Fibre Specifications
Carbon fibre reinforced plastic isa material that will create demand in future for aviation Industry, theautomobile industry, the wind energy sector as well as the shipbuildingindustry. Carbon weaving produces the fabric in Uni Directional Carbon fabric(UD) or Bi Directional Carbon Fabric (BD), according to end use. Fabric can bewoven in different weaves like plain, twill or satin.
Carbon fibre reinforced plastic isextremely light weight, stable and immune to wear and tear.
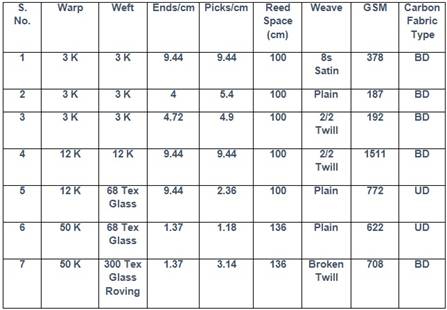
Carbon fibre fabric construction particulars:

Pic 01: Spools of Carbon Fibre
A standard amount of carbon fibre
in thousands bundled in roving form is wound on spools.
1 K Carbon Fibre - 1000 filaments
3 K Carbon Fibre - 3000 filaments
6 K Carbon Fibre - 6000 filaments
12 K Carbon Fibre - 12000
filaments
24 K Carbon Fibre - 24000
filaments
50 K Carbon Fibre - 50000
filaments
We conducted research in Nirma
University, Ahmedabad in the Civil Department to repair damages on extremities
of beams.
Carbonfabric (24 K UD Carbon) for repairing building beams:

Cutting carbon fabric (CF) for
axial beams in construction

Application on final layer applying
resin

Layering of carbon fibre for
flexural beams
In this way for multi-storied old
buildings, the damaged beams can be repaired without removing basic
infrastructure.
Carbon Hybrid Fabrics
Cost effective and composite
applications

Carbon fibre fabric can be woven
with aramid glass for composite application, for aerospace fabric and carbon
rings, carbon rods for artificial limbs, wind energy, sports goods, marine,
automotive and infrastructures.
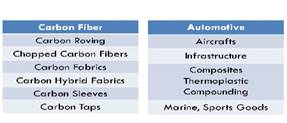
Carbon product variants and applications:
Conclusion:
Properties of CFRP have brought
high safety to motorsports and have also made vehicles more powerful. Moreover,
vehicles with less weight consume less fuel, which is a benefit for everyone's
budget as well as for the environment.
The lightweight potential of CFRP
can be used for many apllications. CFRP leads to making very light and
therefore energy-efficient aircrafts, vehicles and ships as well as larger
rotor blades for more powerful wind turbines. CFRP can lead to the making of
longer bridges, higher buildings or sel-supporting roofs with wider spans.
Although these are some of the
common uses of carbon fibre, many new applications are seen almost daily. The
growth of carbon fibre is fast, and in just five years, this list will be much
longer.
Reference:
1. Fibre2fashion.com
2. Iimts.edu.in
3. Mueller-frick.com
4. Itmaasia.com
5. Teijin.com
6. Research Work at Nirma
University, Ahmedabad
About the author:
Pradeep Kulshrestha is DGM - weaving, Chiripal Group. He has three decades of experience in textiles and research projects in technical textiles and composite applications.